Is your furnace not igniting? Learn common causes & DIY fixes for cold air blues. Get expert tips to troubleshoot your heating system safely.
When Your Furnace Won’t Start: Understanding the Problem
When your home isn’t warming up during Northwest Washington’s harsh winters, a furnace not igniting is a likely culprit. While frustrating, many ignition problems have simple solutions you can handle yourself.
Quick Diagnosis for Furnace Not Igniting:
- Check thermostat settings: Ensure it’s set to “heat” and the temperature is 5°F above the current room temp.
- Verify power supply: Check the furnace switch, circuit breaker, and fuse panel.
- Inspect air filter: Replace if dirty or clogged, as this restricts airflow.
- Confirm gas supply: Ensure the gas valve is open (handle parallel to the pipe).
- Examine ignition system: Check for a pilot light (older units) or listen for an electronic igniter (newer units).
- Safety first: If you smell gas, leave immediately and call 911.
Issues like incorrect thermostat settings, dirty air filters, or tripped circuit breakers are common. However, problems involving gas lines, electronic components, or safety switches require professional attention.
This guide will walk you through common causes of ignition failure, from easy DIY fixes to more complex troubleshooting. We’ll help you know when to tackle the problem and when to call an expert.
Remember: Safety always comes first. If you smell gas or feel unsure about any step, contact a professional HVAC technician.
Why is My Furnace Not Igniting? Common Causes and DIY Fixes
When your furnace not igniting leaves you in the cold, don’t panic. Many heating issues have straightforward solutions you can perform yourself, saving time and money. Start with these simple checks.
Check Your Thermostat

Your thermostat is the command center for your heating system. If it’s not giving the right orders, your furnace won’t start.
- Set to “Heat”: It’s easy to forget to switch from “cool” to “heat” as seasons change.
- Raise the Temperature: Set the temperature at least 5 degrees higher than the current room temperature to signal the furnace to turn on.
- Check Batteries: If your thermostat is battery-powered, replace them with a fresh set. Weak batteries can prevent communication with the furnace, even if the display is on.
- Read Error Codes: Smart thermostats often display error codes that can help diagnose the problem.
If these steps don’t work, it may be time to Contact Us for thermostat issues.
Inspect the Power and Gas Supply
Your furnace needs electricity and fuel to operate. A loss of either will prevent it from igniting.
- Furnace Power Switch: Locate the switch on or near the furnace (it looks like a light switch) and ensure it’s in the “on” position.
- Circuit Breaker: Check your electrical panel for a tripped breaker. It will be in the middle or “off” position. Push it firmly back to “on.” If it trips again immediately, you have an electrical problem that requires a professional.
- Fuse Panel: In older homes, look for a blown fuse, which will appear blackened or have a broken wire inside. Replace it with a new fuse of the exact same amperage.
- Gas Shut-Off Valve: Find the valve on the gas line to your furnace. The handle should be parallel to the pipe, indicating it’s open. If it’s perpendicular, it’s closed.
- Check Other Gas Appliances: See if your gas stove or water heater is working to confirm you have a gas supply to the house.
Critical Safety Warning: If you smell the “rotten egg” odor of natural gas, leave your home immediately and call 911 from a safe distance. Do not use any electronics or light switches.
The Critical Role of the Air Filter
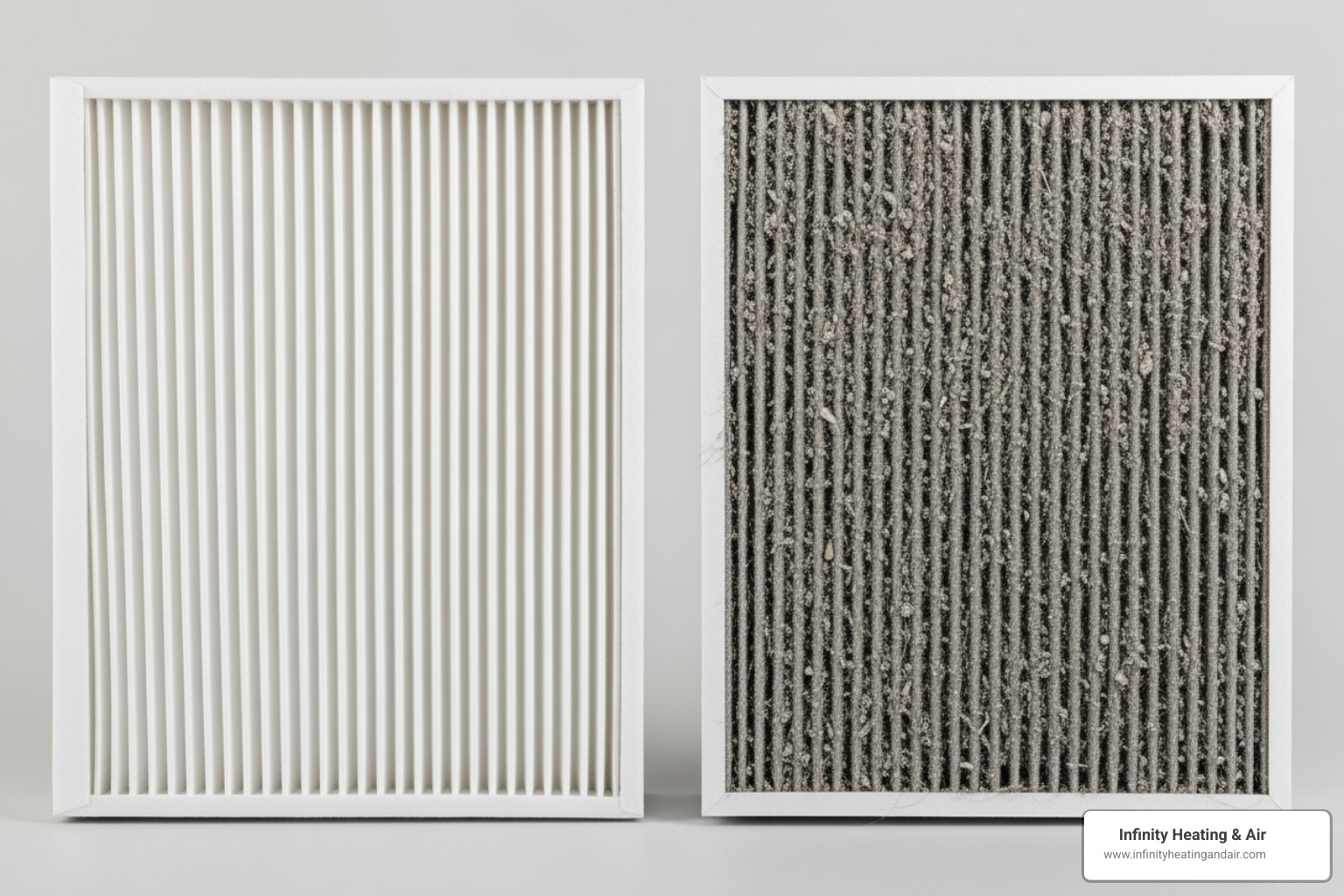

A clogged air filter can prevent your furnace not igniting. It restricts airflow, causing the furnace to overheat and trip a safety limit switch, which shuts the system down before it can ignite.
To check your filter, slide it out of its housing. If you can’t see light through it, it’s time for a replacement. As a general rule, filters should be changed every 1-3 months. Pet owners or those in high pollen areas should change them more frequently, often monthly.
After replacing a clogged filter, you may need to reset your furnace’s power to clear any tripped safety switches. For more comprehensive air quality solutions, explore More about our services.
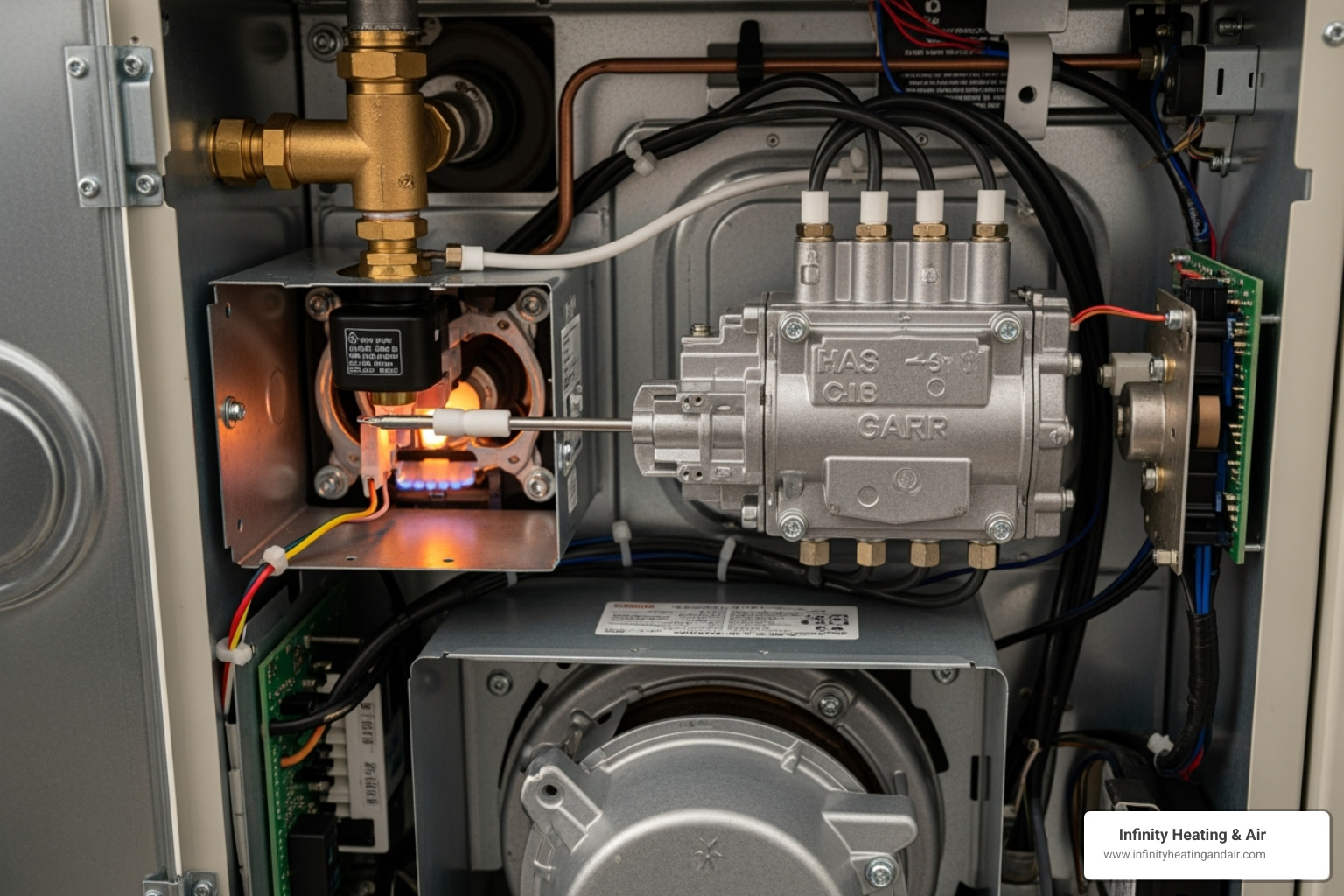
Understanding Your Furnace’s Ignition System
If the basics didn’t solve your furnace not igniting issue, the problem may be with the ignition system itself. Furnaces use different methods to create a flame, and knowing your type is key to troubleshooting.
Older Furnaces: The Standing Pilot Light
Furnaces over 20 years old often have a standing pilot light—a small, continuous flame that ignites the main burners. You can usually see this blue flame through a small opening near the burners.
The most common issue is the pilot light going out due to a draft or a dirty pilot assembly. Relighting instructions are typically printed on a label inside the furnace. The process usually involves turning a knob to “pilot,” pressing it down to start gas flow, and lighting the flame with a long lighter. Hold the knob for 30-60 seconds to heat the thermocouple.
The thermocouple is a safety device that senses the pilot flame’s heat. If the flame goes out, the thermocouple cools and shuts off the gas. If your pilot lights but won’t stay lit, the thermocouple may be dirty, faulty, or misaligned.
Modern Furnaces: Electronic Ignition
Most furnaces from the last 20-30 years use electronic ignition for better energy savings, creating a flame only when heat is needed.
- Hot Surface Igniter (HSI): This is the most common type. A small element heats to a glowing red-hot temperature to ignite the gas.
- Intermittent Pilot System: An electronic spark lights a temporary pilot flame, which then ignites the main burners.
- Spark Igniter: Similar to a gas grill, this system creates rapid sparks to light the main burner gas directly. You’ll hear a distinct clicking sound.
Signs of failure for electronic systems include:
- Glowing but no flame: The igniter is working, but the gas valve may not be opening.
- Clicking sounds without ignition: The spark igniter is trying, but gas isn’t flowing or the spark is too weak.
- No glow or click at all: This points to a faulty igniter or a problem with the furnace’s control board.
| Feature | Standing Pilot Light | Electronic Ignition |
|---|---|---|
| Pros | Simple, reliable mechanism; easy to relight | More energy-efficient; safer operation; higher efficiency ratings |
| Cons | Wastes gas with constant flame; easily blown out | More complex components; sensitive to power issues; replacement can be costly |
| Common Issues | Pilot light extinguished; faulty thermocouple | Igniter burnout or cracking; control board failures; flame sensor problems |
Understanding your system is the first step. Electronic ignition problems are a very common reason for a furnace not igniting.
Advanced Troubleshooting: When the Basics Don’t Work
If you’ve checked the thermostat, power, and filter, but your furnace not igniting remains a problem, it’s time to look at specific components. Your furnace follows a precise “sequence of operation” for safety, and a failure at any step will halt the process.
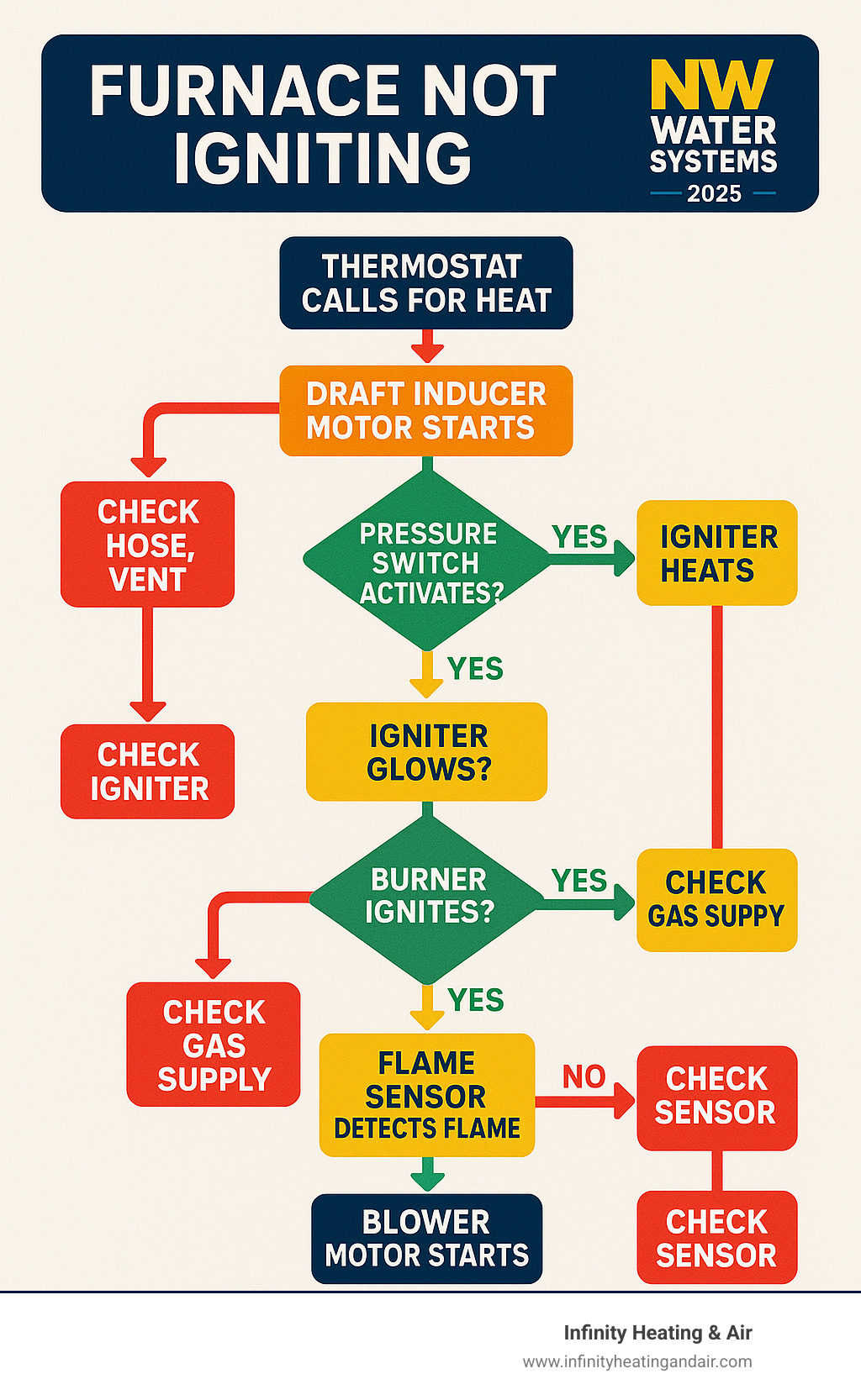
Here’s the normal startup sequence:
- The thermostat calls for heat.
- The draft inducer motor starts (a humming sound) to vent exhaust gases.
- A pressure switch confirms the vent is clear.
- The igniter activates (glowing red or clicking).
- The gas valve opens (a soft click), and gas flows to the burners.
- The burners ignite.
- A flame sensor confirms the flame is present.
- The blower motor starts, circulating warm air.
Noting where this sequence fails can help pinpoint the problem.
The Igniter Glows, But Burners Don’t Light
If the igniter glows but the burners don’t light, the issue is likely with the fuel delivery. Common causes include:
- Faulty Gas Valve: The valve may not be opening to release gas. You should hear a distinct “click” when it activates. If not, the valve may be stuck or not receiving power, which requires a professional.
- Low Gas Pressure: The valve may open, but insufficient gas pressure prevents proper flow to the burners.
- Dirty Gas Burners: Dust and rust can clog the burner ports, blocking gas flow and preventing ignition.
- Dirty or Faulty Flame Sensor: Even if the burners light briefly, a dirty flame sensor can fail to detect the flame and shut the system down immediately as a safety precaution.
- Control Board Failure: The furnace’s control board might be sending power to the igniter but failing to signal the gas valve to open.
For these more complex issues, it’s best to seek professional help. See our Information on our inspection process to learn how we diagnose these problems.
Diagnosing a Faulty Flame Sensor
The flame sensor is a critical safety device. It detects the flame and shuts off the gas supply if ignition fails, preventing dangerous gas buildup.
Signs of a dirty sensor include furnace short cycling: the furnace ignites, runs for a few seconds, and then shuts down. This happens because carbon buildup on the sensor rod insulates it, preventing it from detecting the flame.
To safely clean the sensor rod, first turn off all power to the furnace at the switch or circuit breaker. Locate the sensor—a thin metal rod with a single wire, positioned in the path of the flames. Unscrew its mounting bracket and gently remove it. Use fine-grit sandpaper or steel wool to lightly polish the metal rod until it’s clean. Reinstall the sensor, restore power, and test the furnace. If cleaning doesn’t work, the sensor may need replacement, which is a job for a professional.
Safety First: When to Call for Professional Help
While many furnace issues are DIY-friendly, some problems require professional expertise. Knowing when to call an expert is a smart way to protect your family and your home.
The Dangers of a Gas Leak
If you smell the distinctive “rotten egg” odor of natural gas, you must act immediately. This is not a DIY situation.
- Evacuate Immediately: Get everyone out of the house.
- Do Not Create a Spark: Do not use light switches, appliances, or even your phone inside the house.
- Call for Help: Once you are a safe distance away, call 911 and then your gas company.
Gas leaks can lead to fires or explosions. For more information, review these natural gas safety guidelines. Your safety is the top priority.
Signs You Need an HVAC Technician for a Furnace Not Igniting
Your furnace will often provide clear signals that it’s time to call a professional. Look for these warning signs:
- Repeatedly tripping circuit breaker: This indicates a potential short circuit or other electrical fault.
- Burning smells: Odors of burning plastic or electrical components suggest overheating parts.
- Loud noises: Banging, clanking, or scraping sounds often point to mechanical failure in the blower or inducer motor.
- Water pooling around the furnace: This can signal a clogged condensate drain or a cracked heat exchanger in high-efficiency units.
- Confusing error codes: While helpful, some codes require specialized knowledge to diagnose and fix.
- Furnace is over 15 years old: If an older furnace has ignition issues, a professional can help you decide if a repair or replacement is the better investment.
If you’re facing a persistent furnace not igniting problem or feel uncertain about any repair, trust your instincts and call a licensed HVAC technician.
Why Professional Furnace Maintenance is Crucial
Regular professional maintenance is the best defense against unexpected furnace failures. It’s a proactive step to ensure your system runs reliably all winter.
During an annual tune-up, a technician will:
- Prevent Ignition Failure: Clean key components like the igniter, flame sensor, and burners to remove buildup that causes most ignition problems.
- Ensure Safety and Efficiency: Check for carbon monoxide leaks, inspect the heat exchanger for cracks, test safety controls, and identify inefficiencies that increase energy bills.
- Extend Your Furnace’s Lifespan: A well-maintained system runs more smoothly and is less prone to major failures, often lasting beyond the typical 15-20 year lifespan.
Our comprehensive annual furnace maintenance services are designed to keep your system running reliably and safely. We are committed to crafting an environment for endless comfort and health in your home.
Frequently Asked Questions about Furnace Ignition
Homeowners in Northwest Washington often have similar questions about why their furnace not igniting. Here are answers to the most common ones.
My furnace clicks repeatedly but won’t ignite. What does that mean?
That clicking is likely the spark igniter trying to light the gas. If the furnace doesn’t ignite, it could mean:
- The gas valve isn’t opening, so there’s no fuel.
- The spark igniter is dirty or faulty and producing a weak spark.
- The flame sensor is faulty and shutting the system down immediately after a brief ignition.
How can I tell if my furnace igniter is bad?
It depends on the type of igniter:
- Hot Surface Igniter (glowing type): Look for visible cracks or white spots. If it doesn’t glow bright orange-red during startup, or doesn’t glow at all, it has likely failed.
- Spark Igniter (clicking type): If you hear the clicking but don’t see a visible spark between the electrodes, the igniter or its control module is likely faulty.
Replacing a faulty igniter is a common repair that quickly resolves many ignition issues.
What is the difference in troubleshooting an old vs. a new furnace?
The age of your furnace changes the troubleshooting approach due to different ignition technologies.
- Older Furnaces: These typically have a standing pilot light. Troubleshooting often involves checking if the pilot is lit and if the thermocouple (the sensor next to the pilot) is working correctly. Relighting the pilot is a common fix.
- Newer Furnaces: These use electronic ignition and a control board. They often display error codes that point to a specific problem with a component like the hot surface igniter, flame sensor, or pressure switch. Troubleshooting involves interpreting these codes and testing the indicated part.
If your gas furnace igniter isn’t working, the cause can range from a simple fix to a more complex problem. It’s important to diagnose it correctly, especially as Northwest Washington temperatures drop.
Get Your Heat Back with Confidence
A furnace not igniting is a solvable problem. By following this guide, you can confidently address the most common issues.
Always start with the basics: check the thermostat, power supply, gas valve, and air filter. These simple steps resolve a surprising number of heating problems. If the issue persists, use your knowledge of your furnace’s ignition system to investigate further.
Prioritize safety above all. If you smell gas, evacuate immediately and call 911. For issues like a repeatedly tripping breaker, strange noises, or any problem that feels beyond your skill level, calling a professional is the smartest and safest choice.
When you’ve exhausted the DIY options, trust the certified technicians at Infinity Heating & Air to restore your home’s warmth. We’re here to get your heating system back on track safely and efficiently, especially during Northwest Washington’s cold winter months.
Need Service?





